History
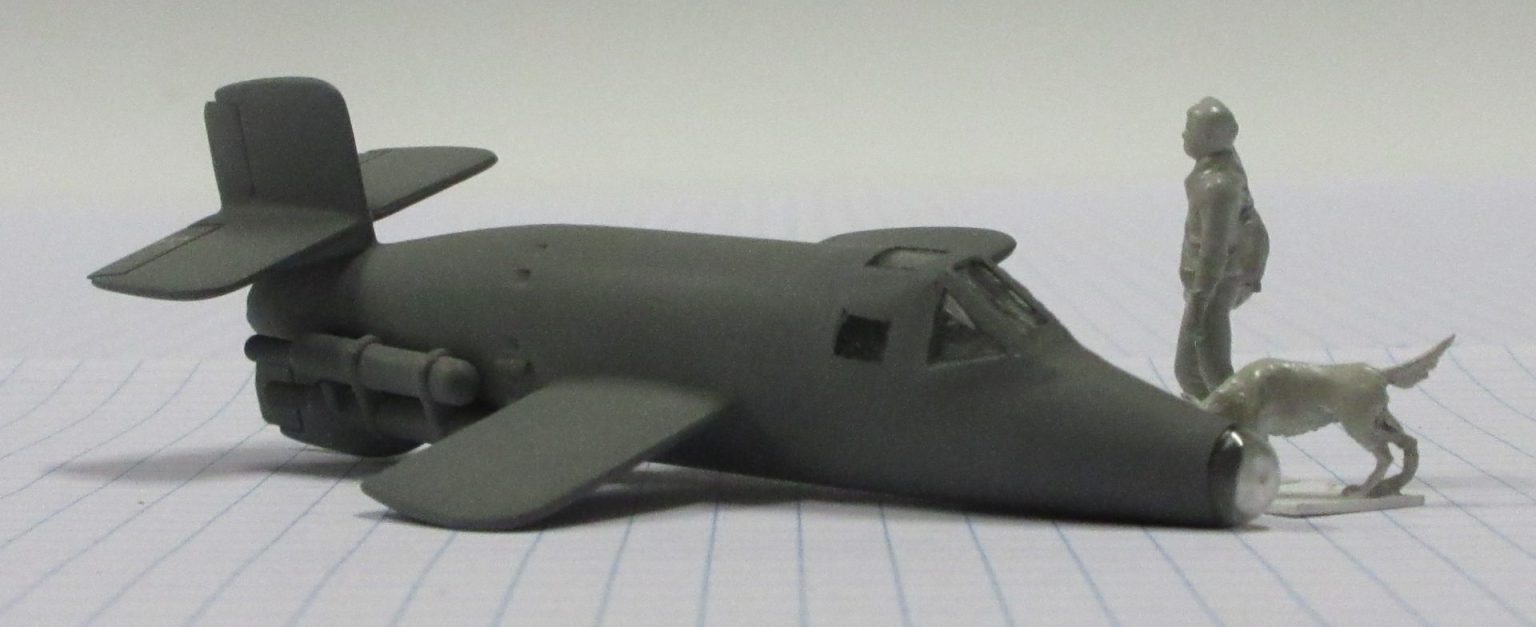
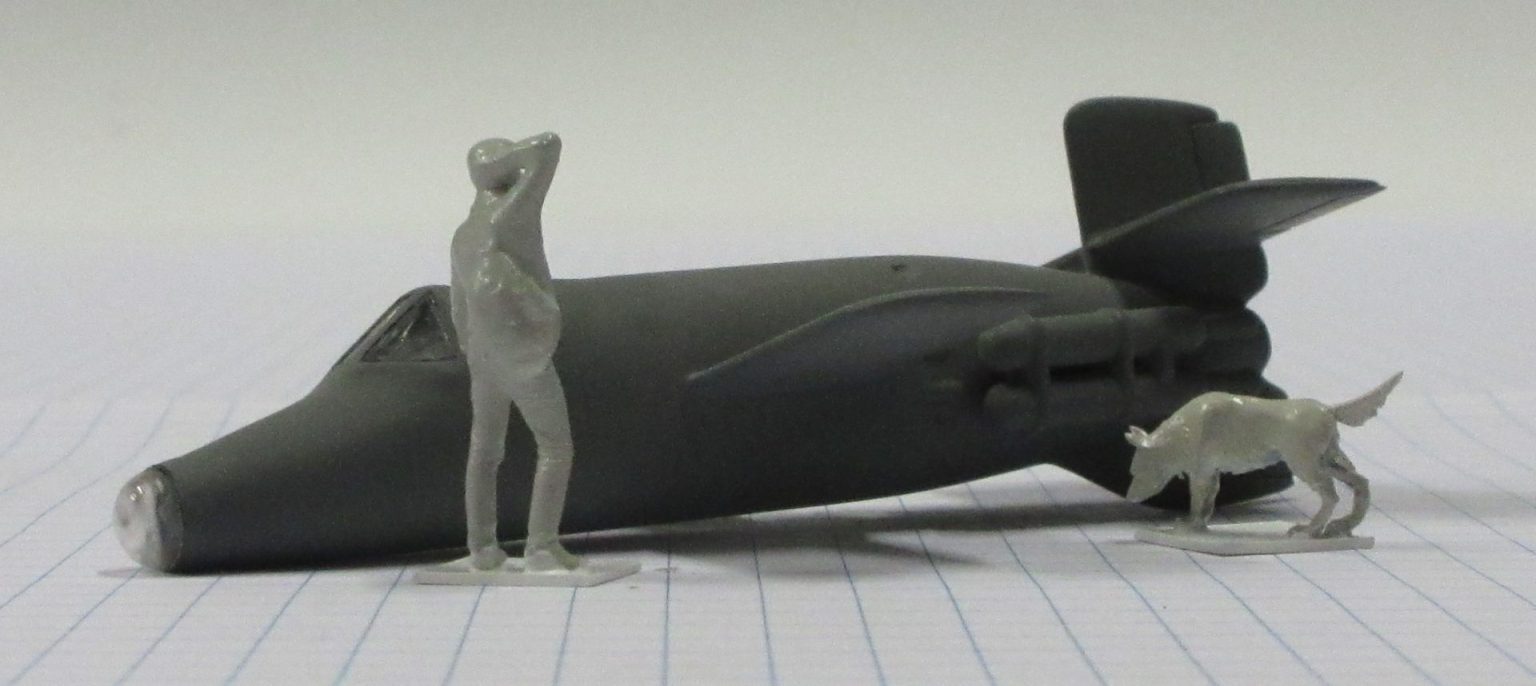
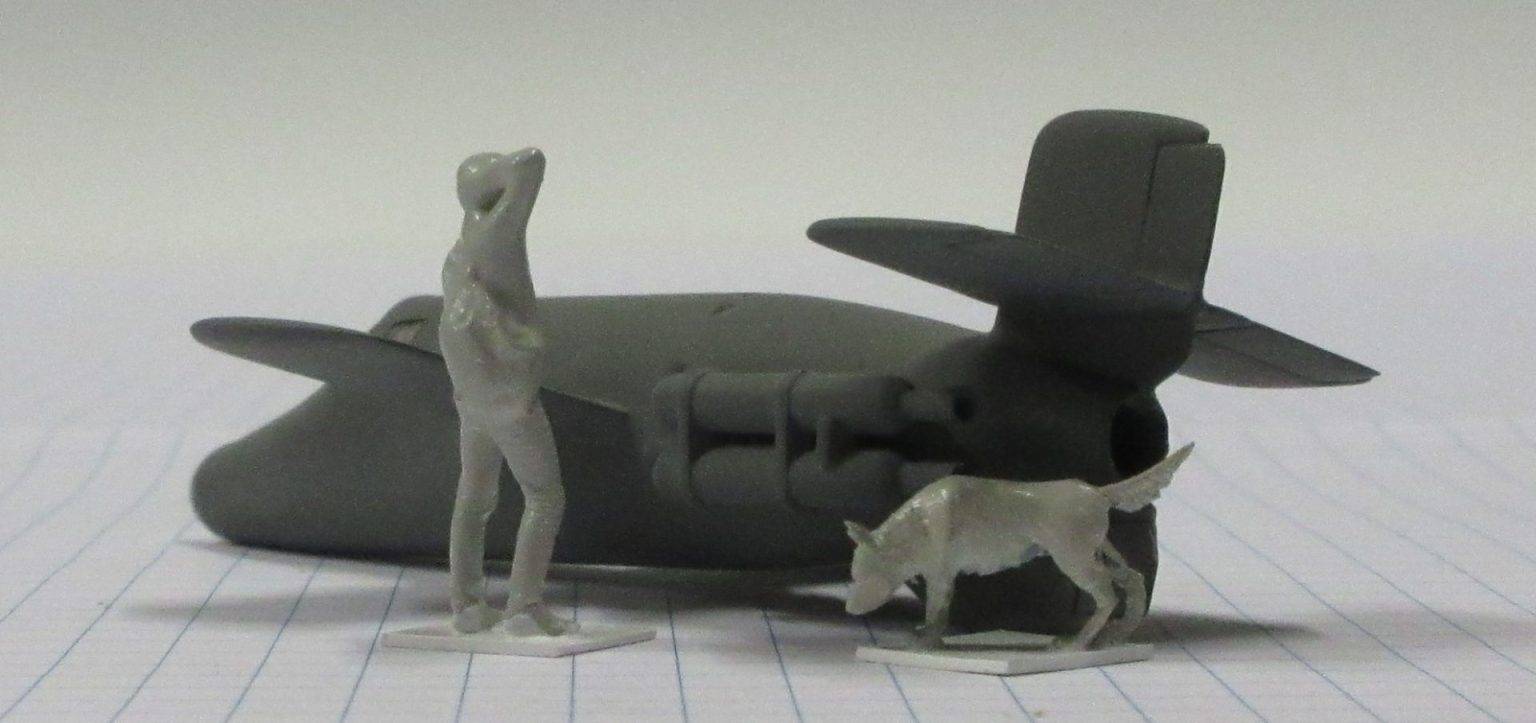
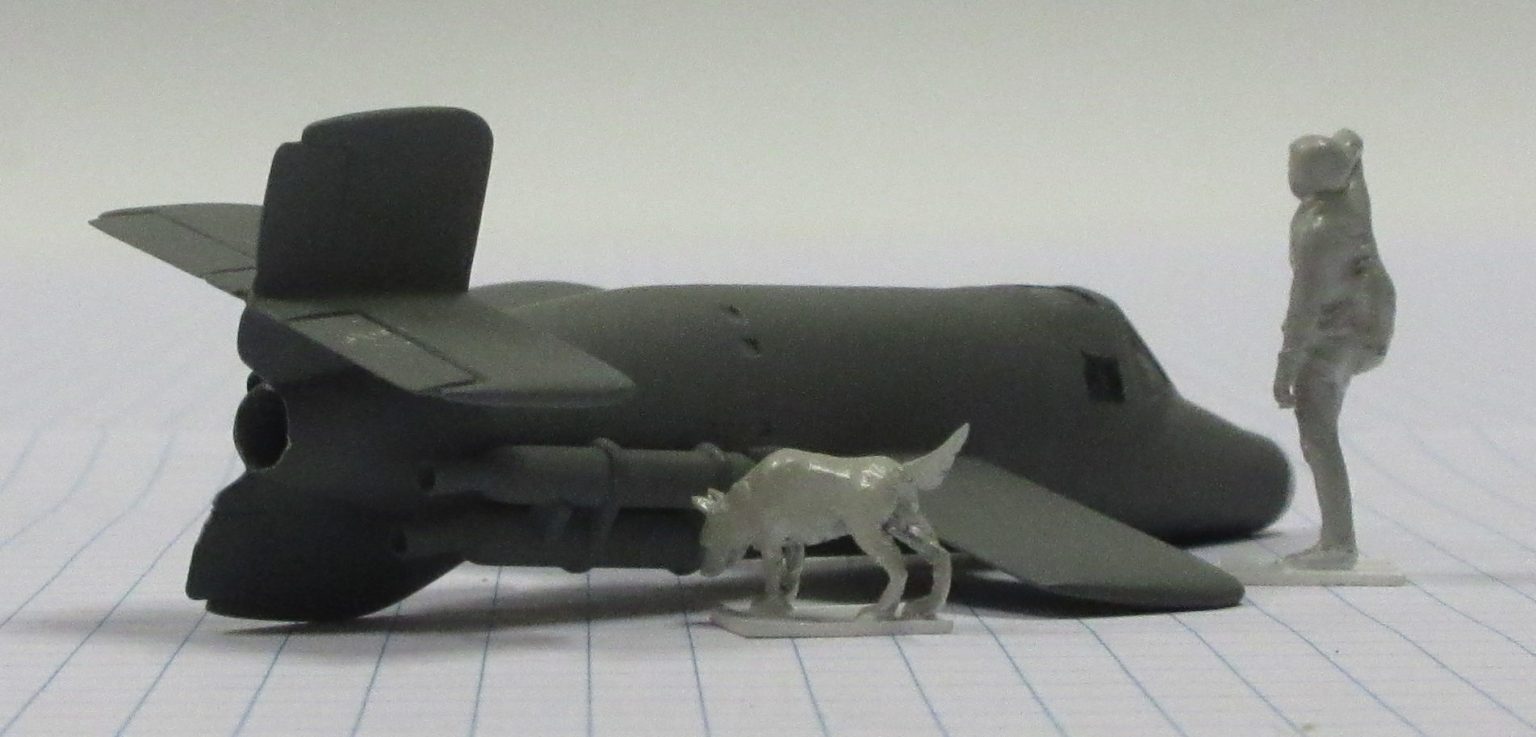
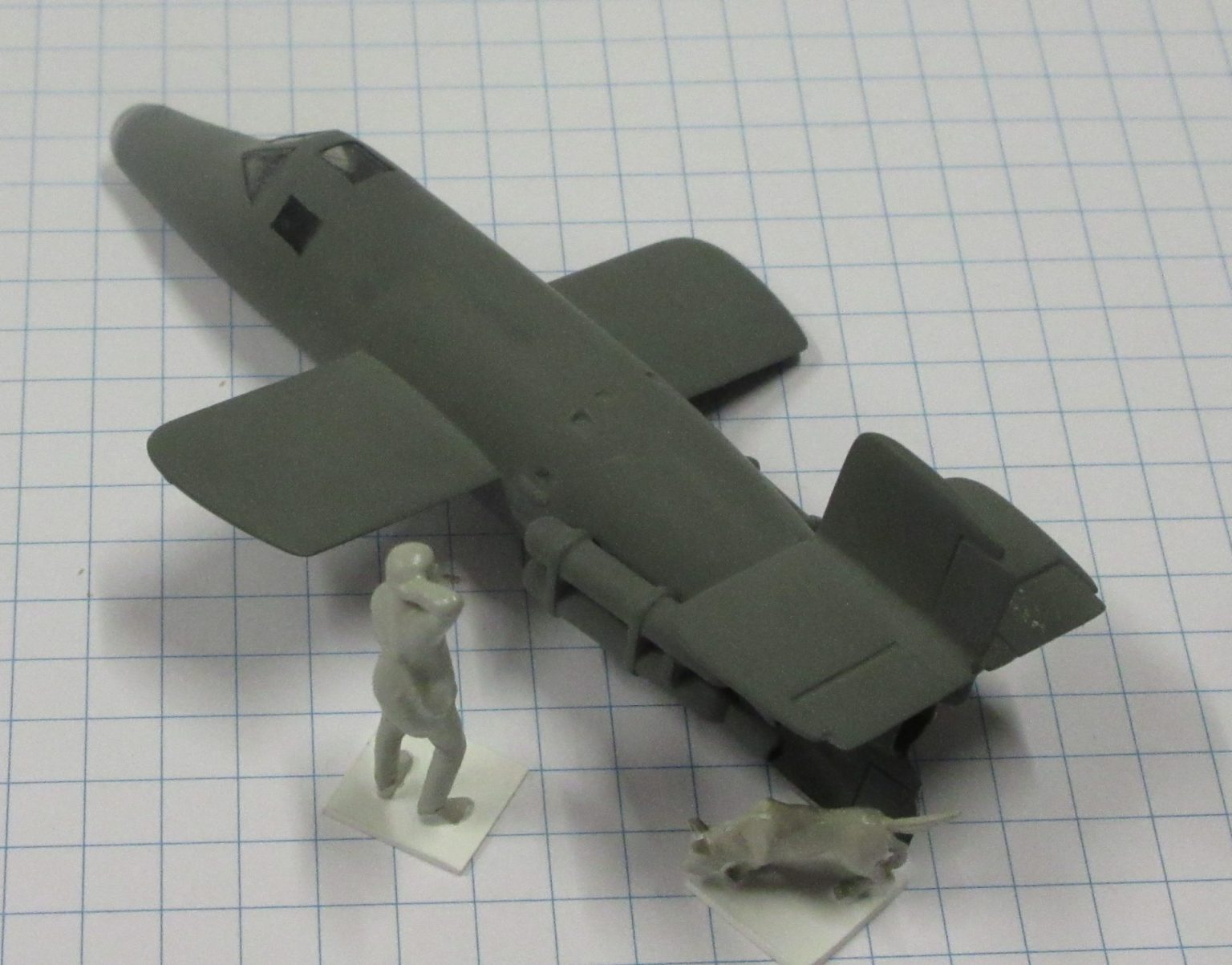
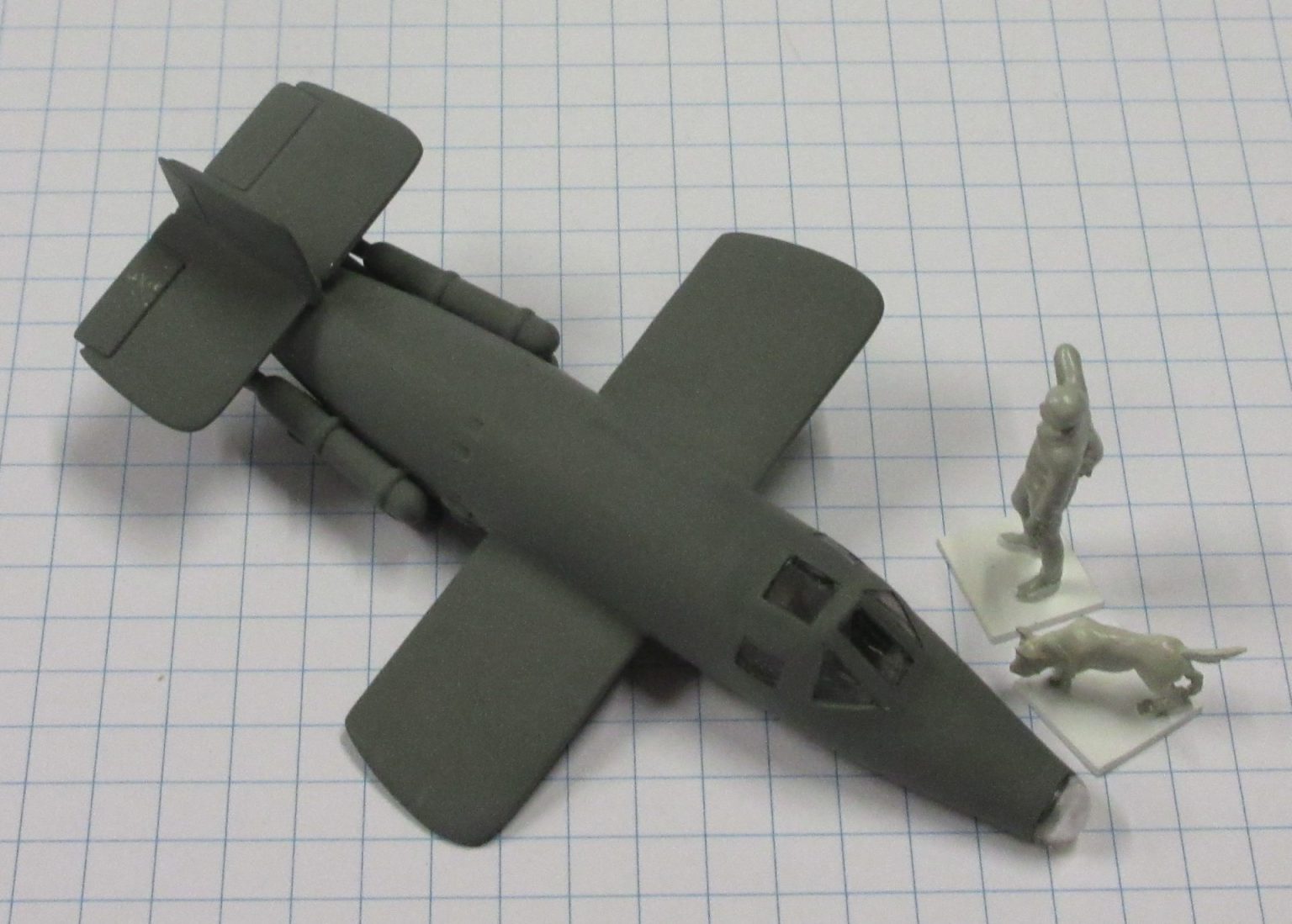
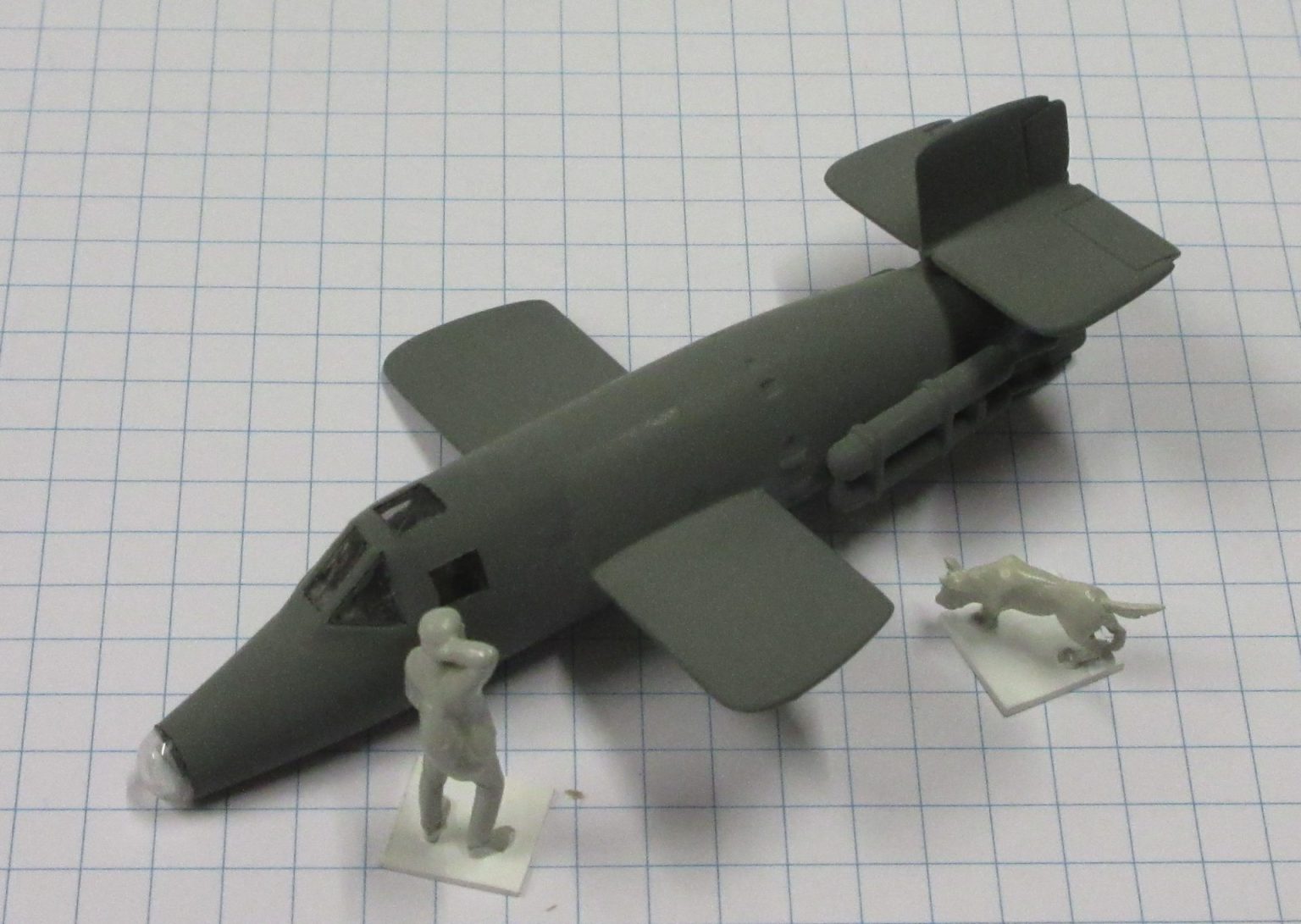
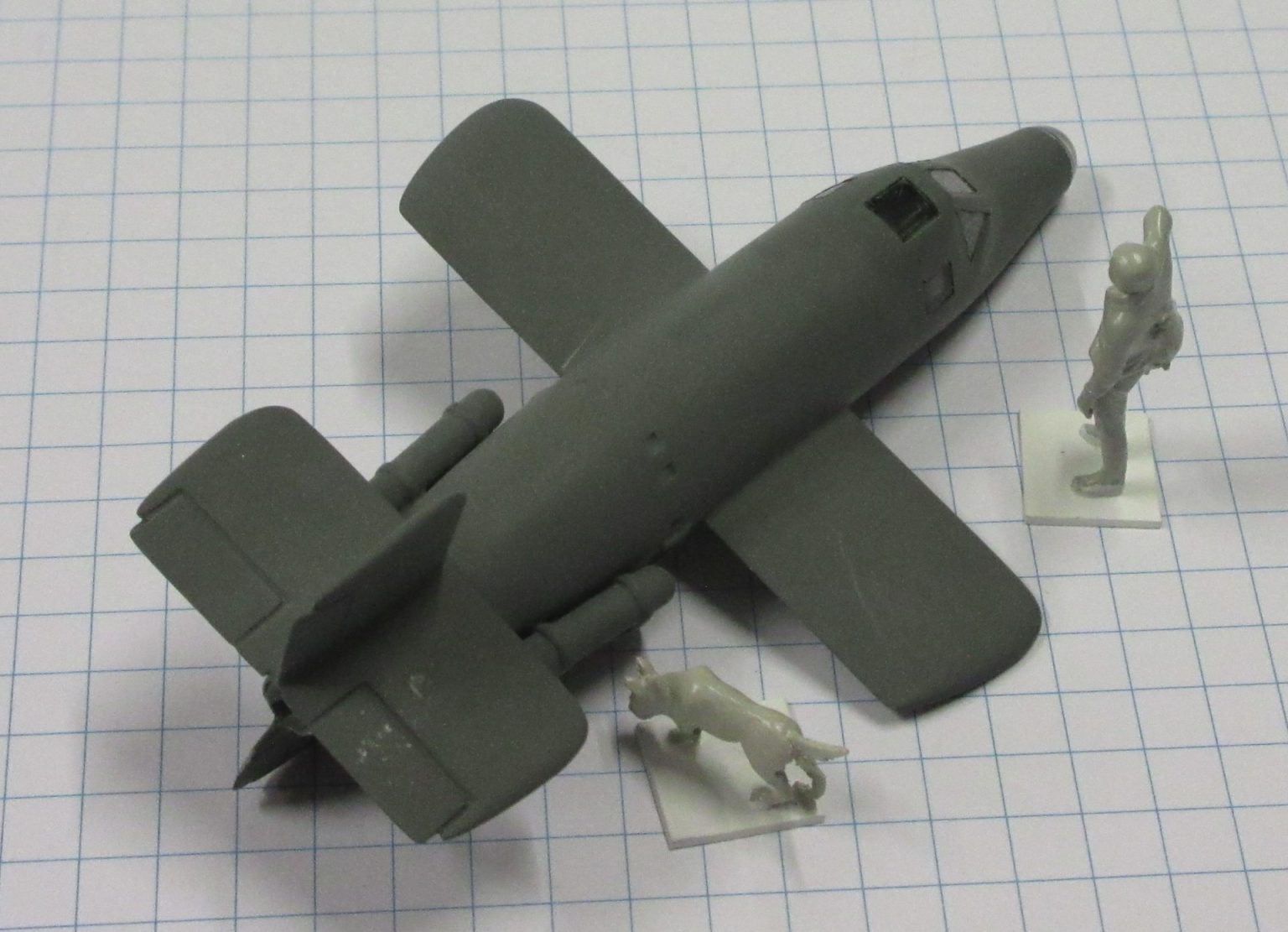
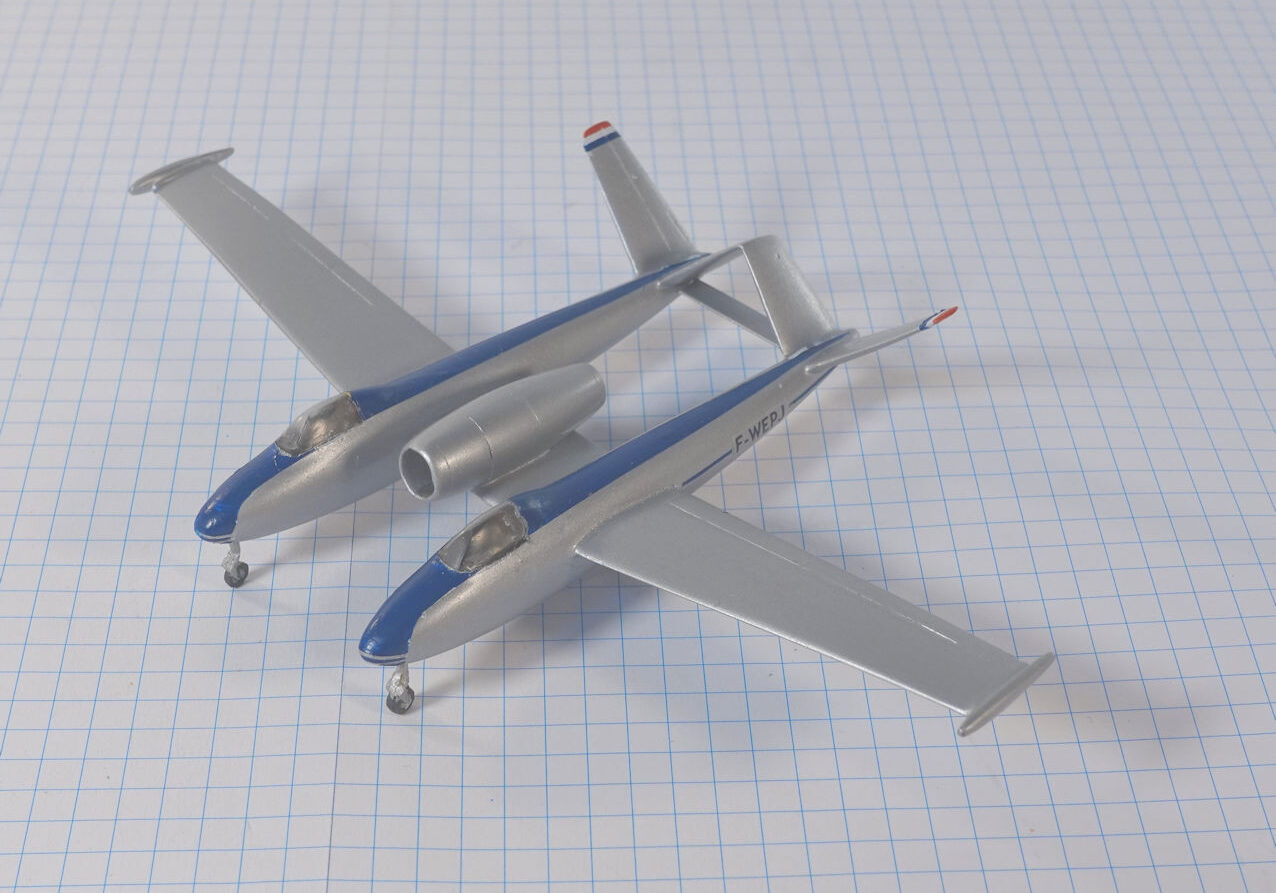
The Bachem Natter (Viper) was developed by Germany towards the end of World War II. In essence it was surface-to-air missile in which guidance was provided by a pilot. None were flown in action.
As Germany struggled under the weight of allied bombing from 1943 new and desperate means of shooting down bombers were needed.
The Bachem Natter was an ingenious weapon, a vertically launched rocket that would climb rapidly to intercept bombers and attack them with powerful short range rockets or high calibre cannon.
After the attack the pilot would parachute to the ground, as would the rocket motor.
In the first test firing in February 1945 the pilot was killed but later tests were more successful.
In April 1945 nine Natters were deployed operationally but they were overrun by allied soldiers before they could be used.
This model represents a prototype Natter.
Heller 1/72 kit completed by Leigh Edmonds in April 1997.