History
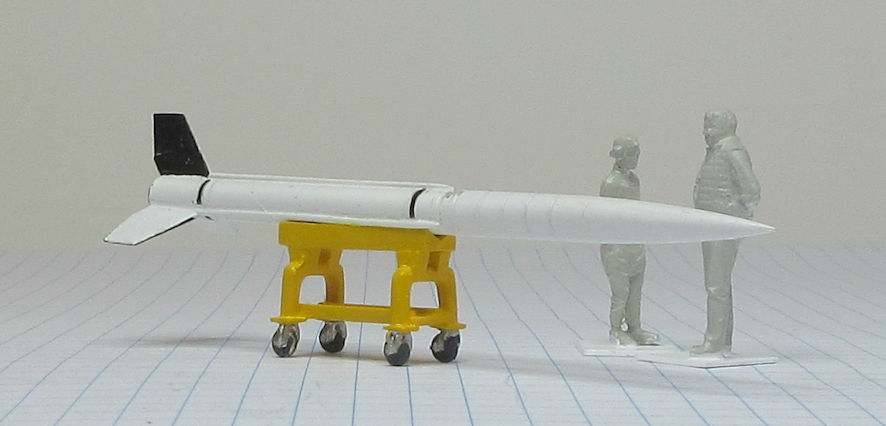
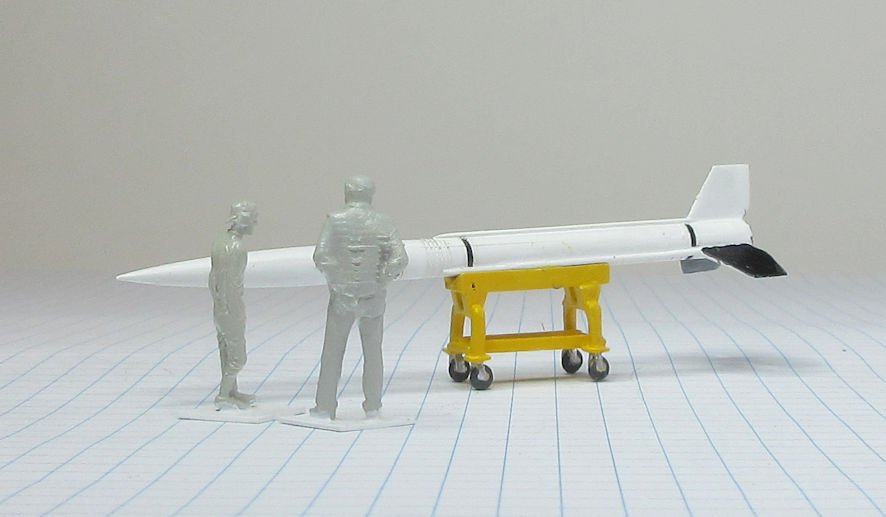
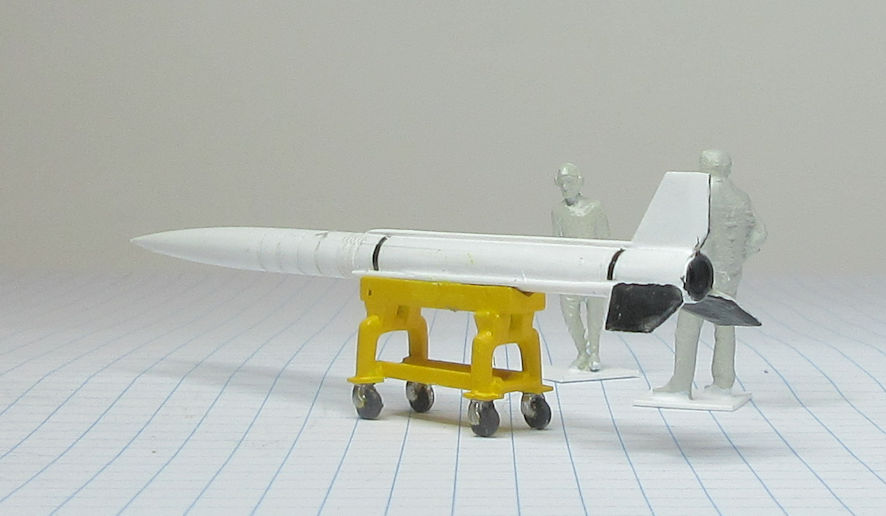
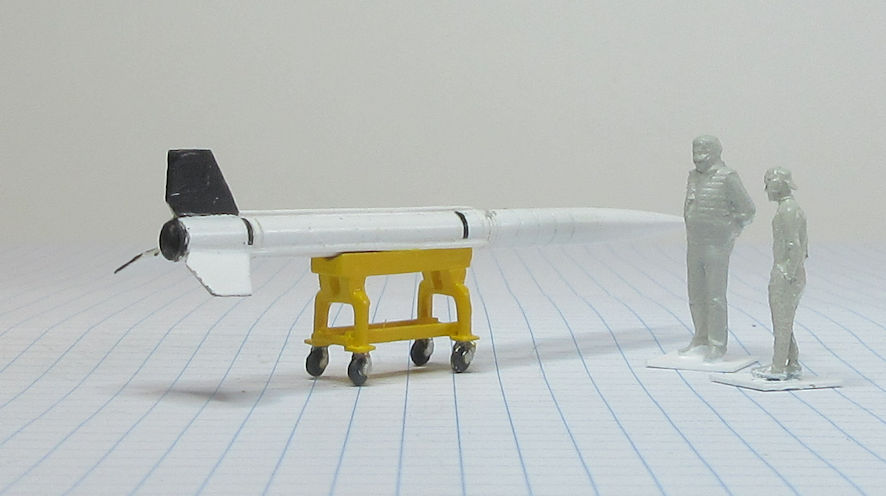
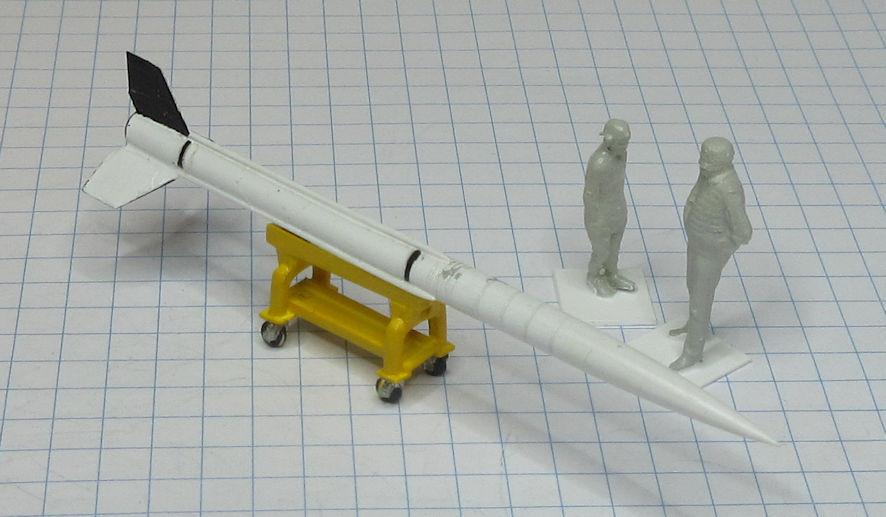
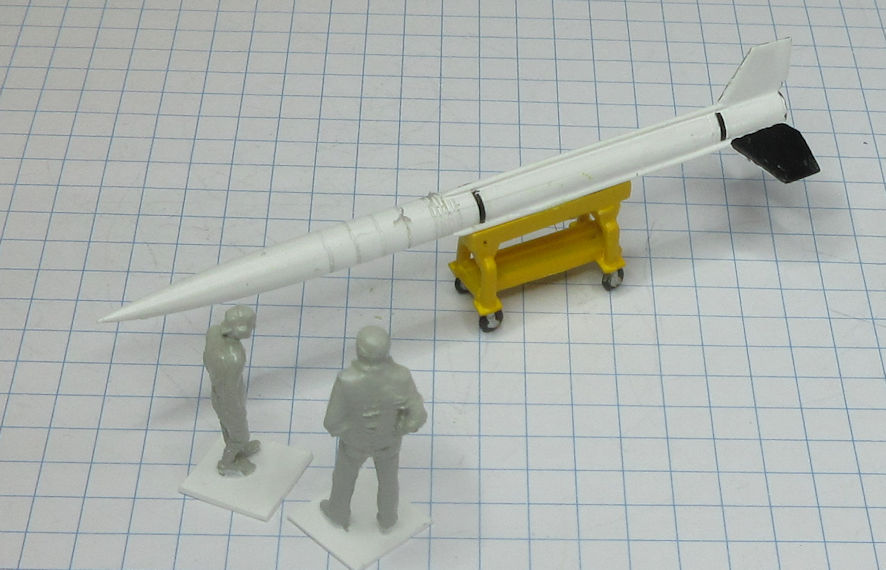
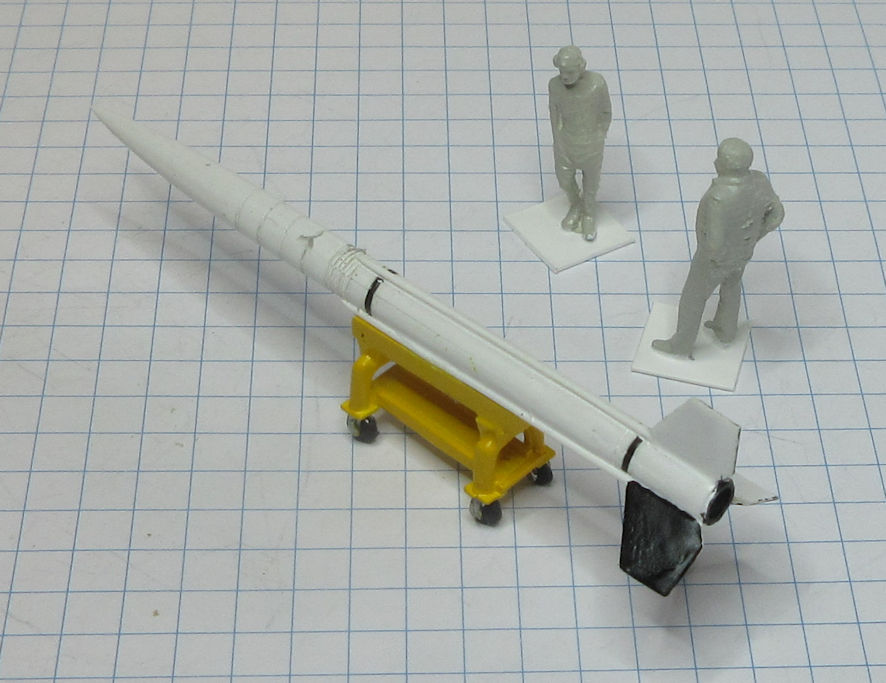
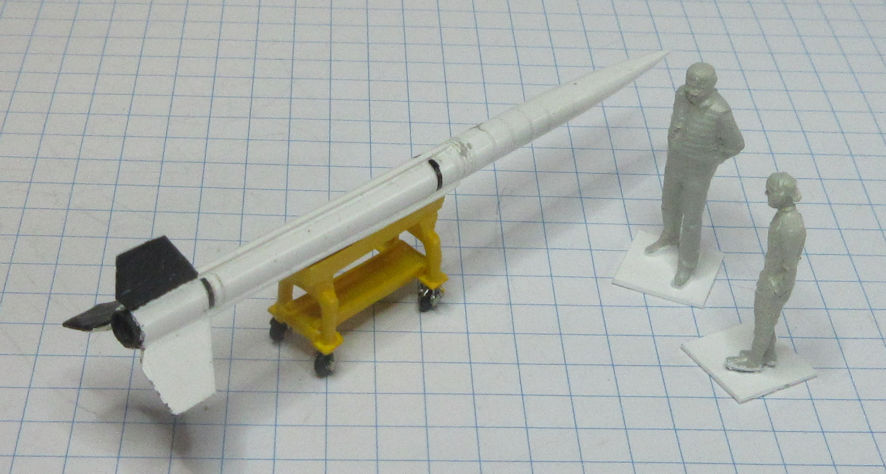
The Aerojet General X-8 was an unguided spin stabilised sounding rocket developed in the United States in the late 1940s and used in the early 1950s. They conducted a wide range of upper atmosphere scientific experiments.
After World War 2 the United States had parts for about 100 German V-2 rockets which it used for various military and upper atmosphere experiments.
When this supply began to run down the government looked for a replacement sounding rocket to use in conducting upper atmosphere experiments and selected the Aerojet General Aerobee which was developed between June 1946 and November 1947 and renamed the X-8.
Sixty-six X-8s were made, half with a slightly more powerful engine. They were used from December 1949 to December 1956 carrying a very wide range of experimental payloads in the nose cone that were returned to earth by parachute after the flight.
This model represents a standard X-8 in the early 1950s.
Data: Engine Aerojet XASR-2 liquid fuel rocket of 12kN thrust. Wing span 1.6m. Length 6.12m. Loaded weight: 489kg. Maximum speed 6,470km/h. Service ceiling 24.3km. Payload 68 to 136kg.
Anigrand 1:72 kit. Completed in October 2017.