History
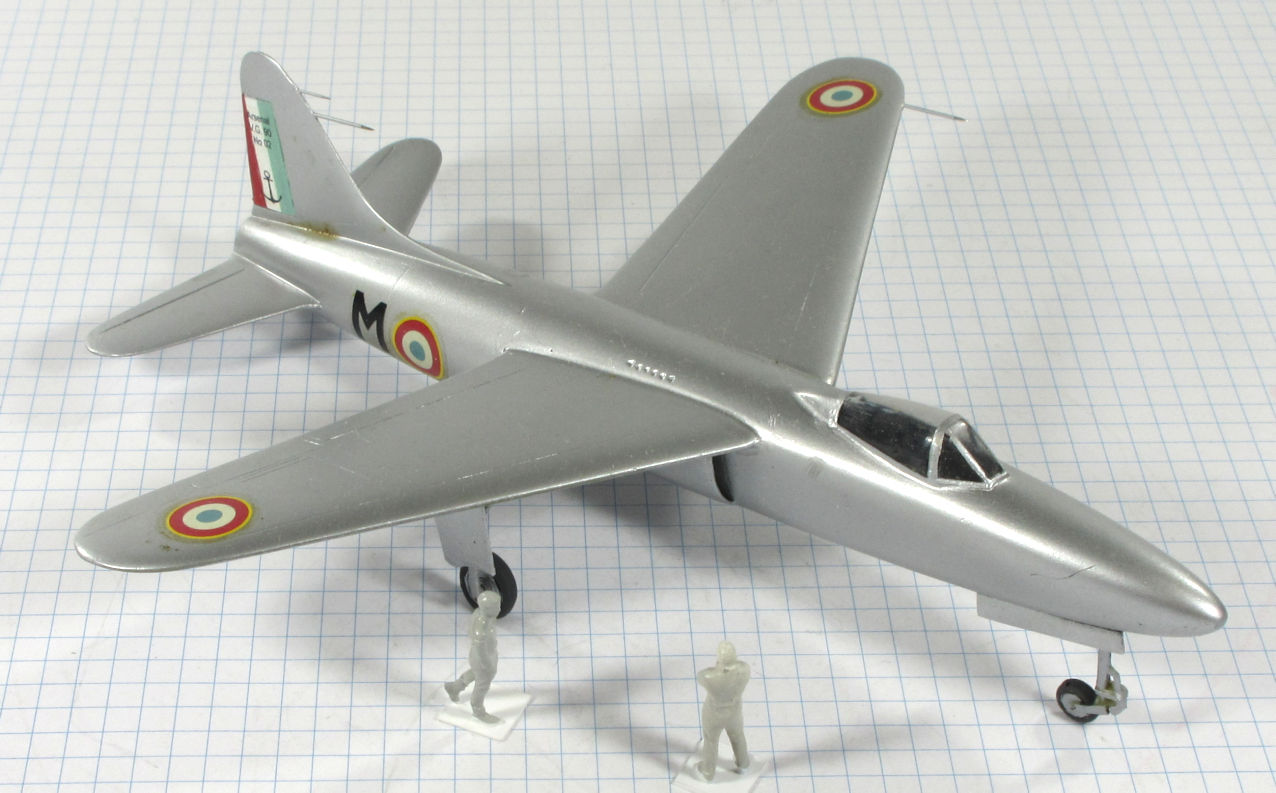
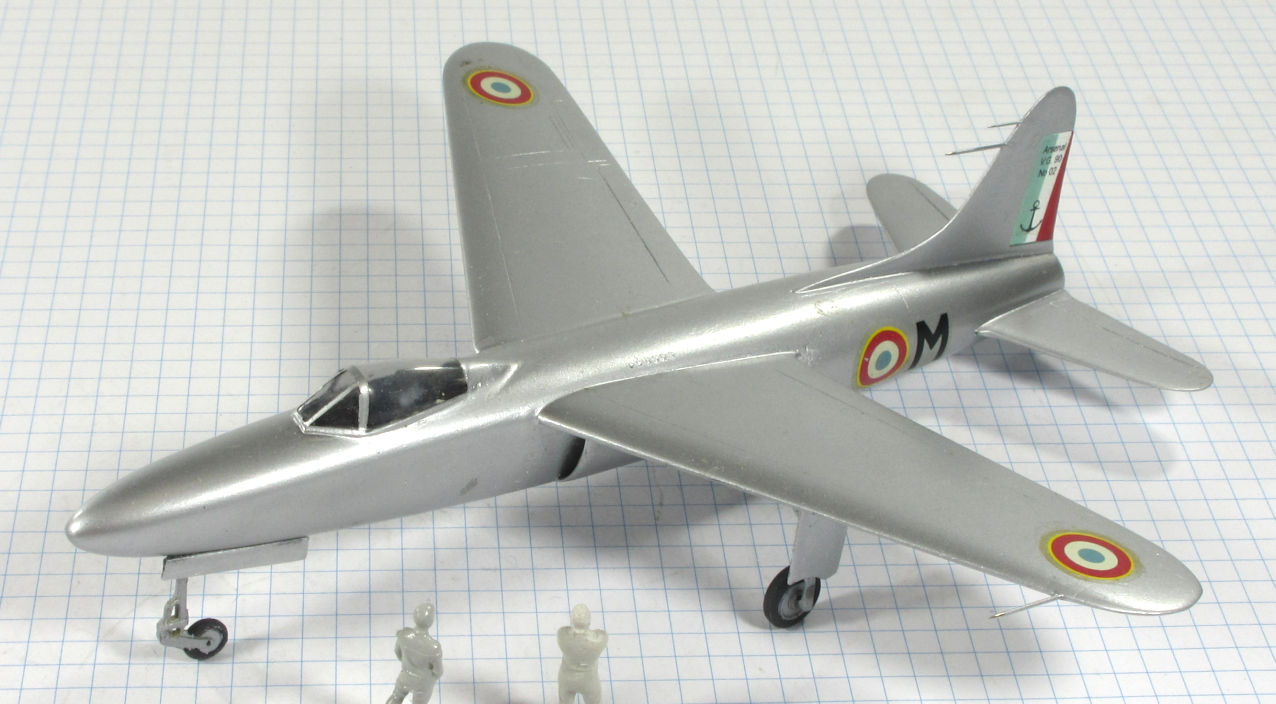
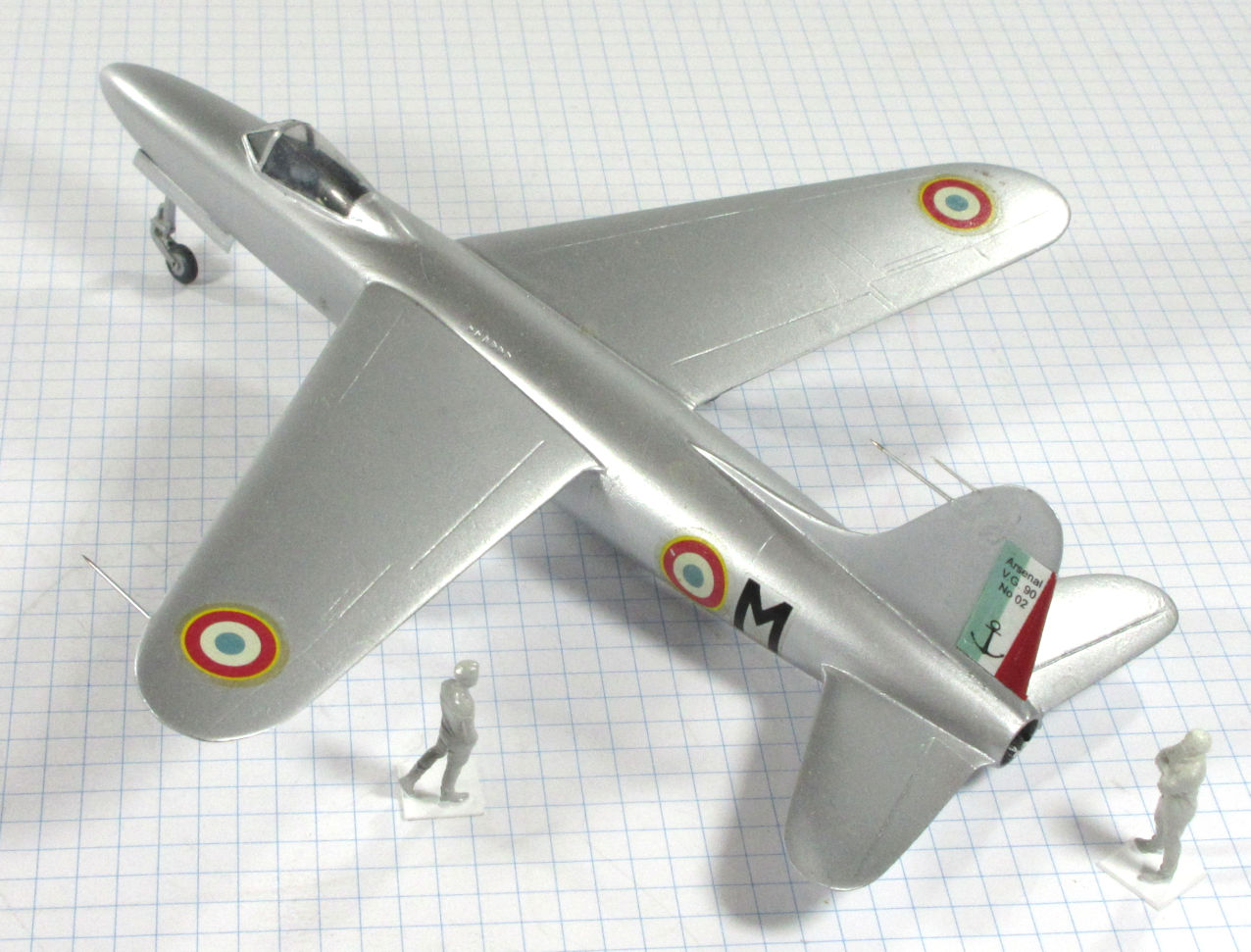
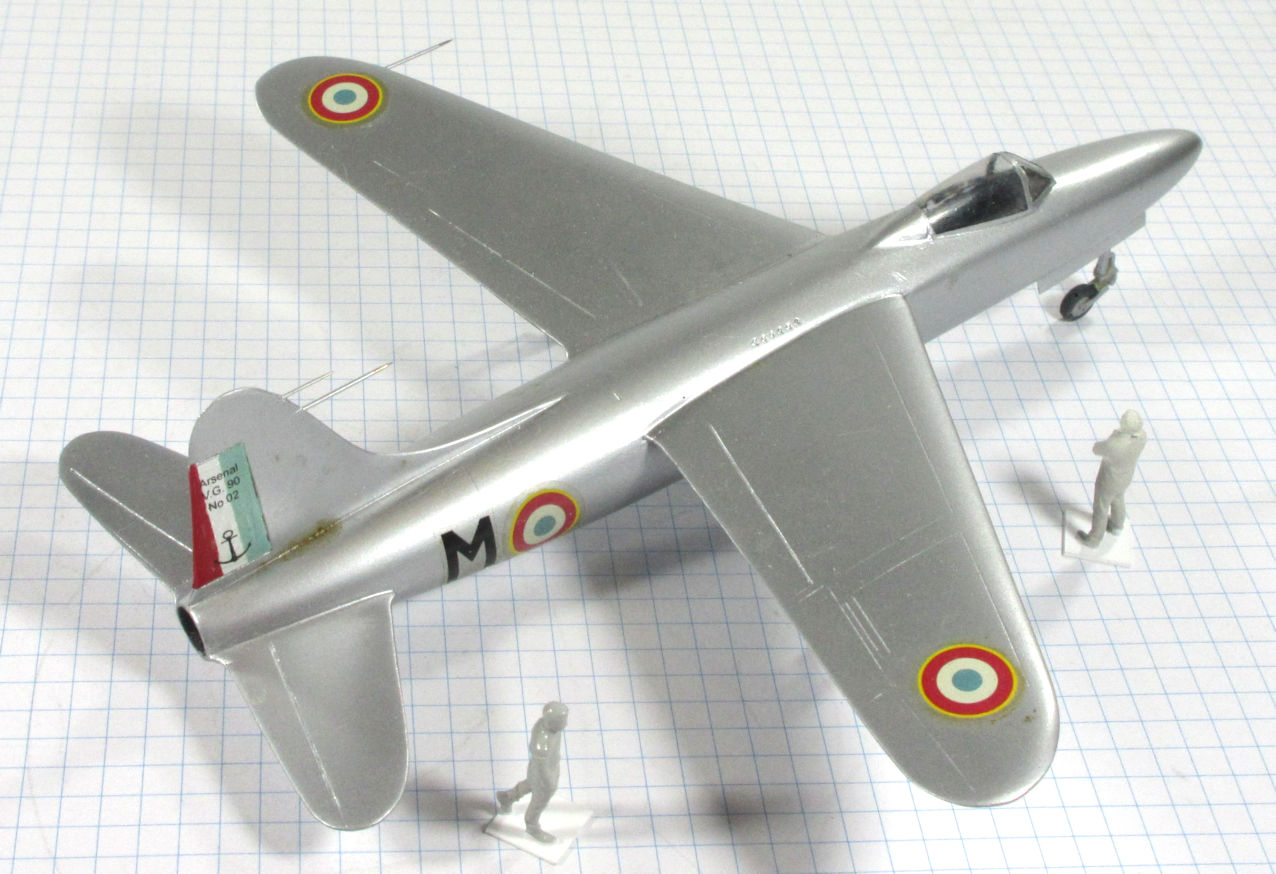
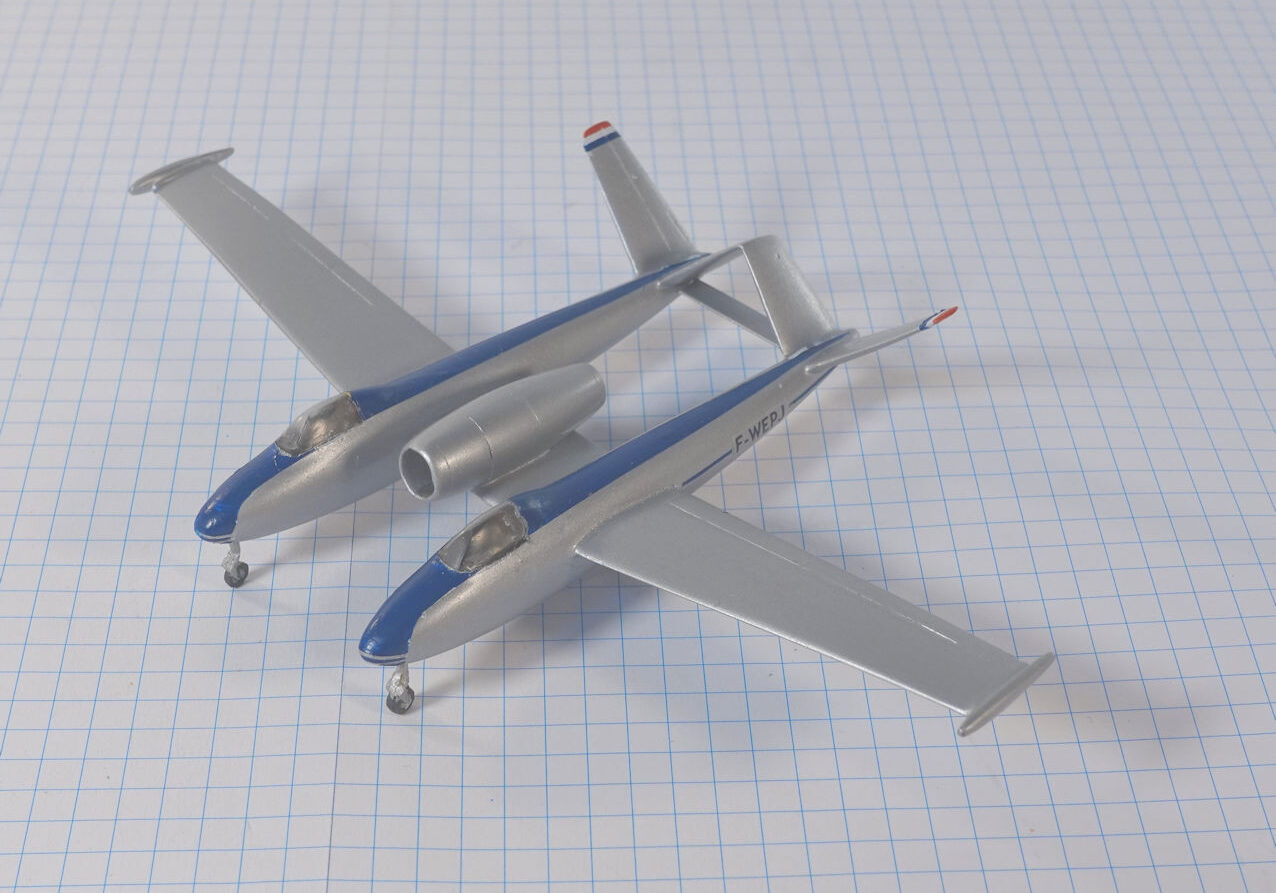
The Arsenal VG.90 was designed to meet the French Navy’s requirement for a jet powered strike fighter in the late 1940s. Although it was chosen for development it was not successful and only two prototypes were built.
After World War II the French aviation industry quickly began developing modern jet powered aircraft. Among them was the Arsenal VG.70 powered by a German Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet.
In 1949 the French Navy issued a requirement for a new carrier capable strike fighter and the Arsenal VG.90, a development of the VG70, was selected from a field of three French proposals.
Two prototypes were built, the first one flying on 27 September 1949 and the second in June 1951.
The first one crashed in May 1950 and the second in February 1952, and the French Navy selected the deHavilland Sea Venom as its jet strike fighter.
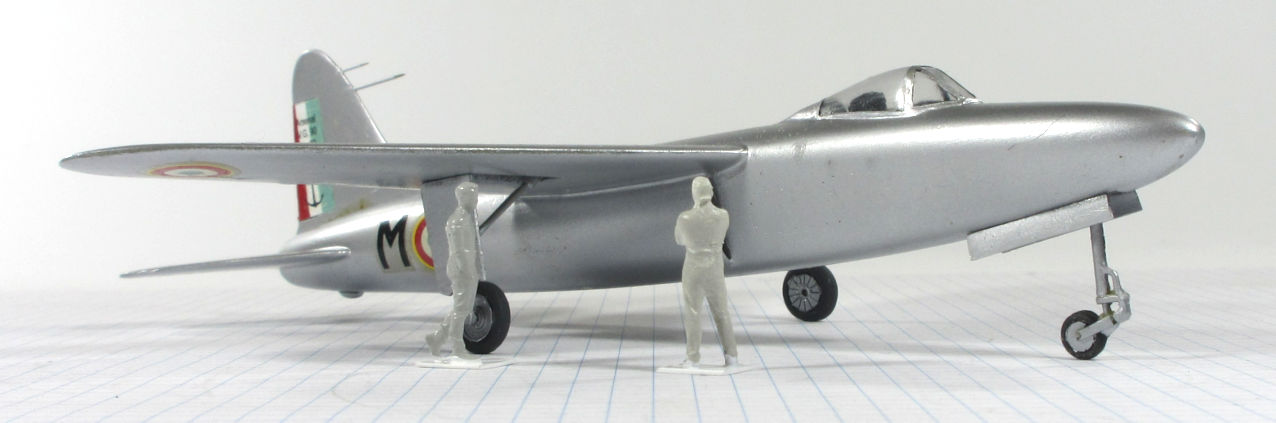
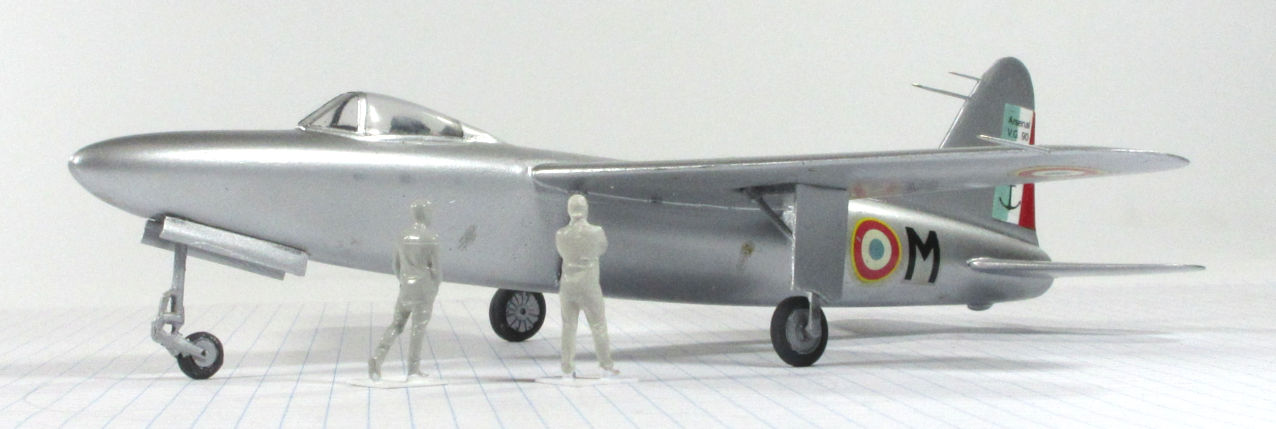
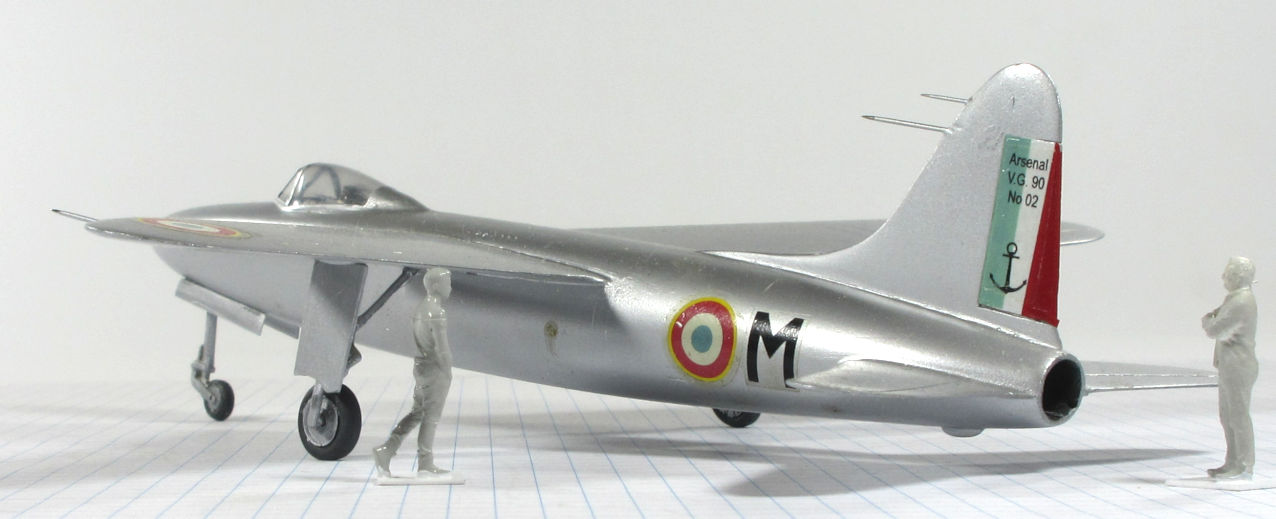
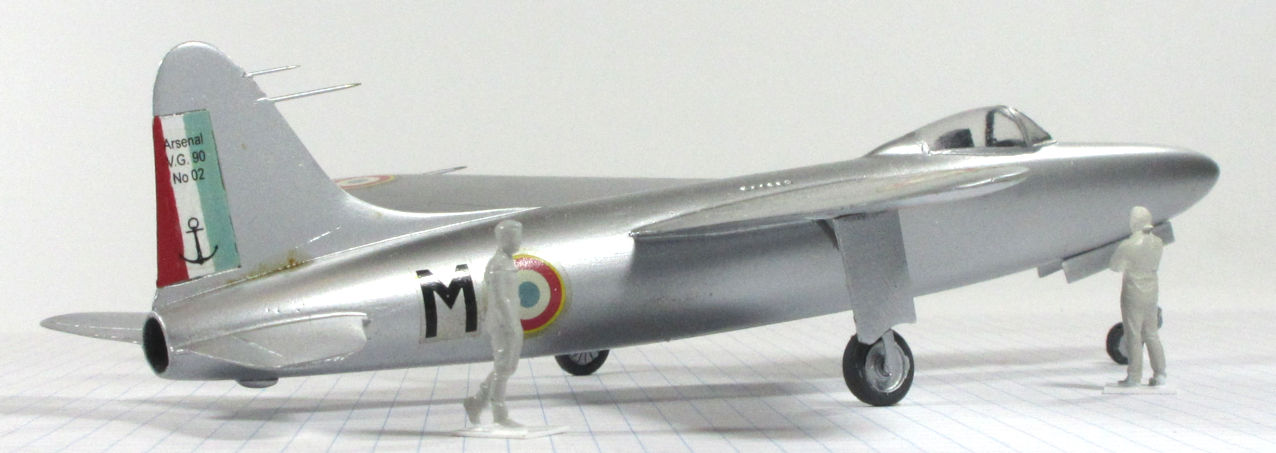
This model represents the secong VG.90 prototype, c.1951.
Dujin 1:72 kit completed by Leigh Edmonds in December 2008.